
A citation style in research refers to a standardized format or set of rules for citing sources and references in academic and scholarly work. To prevent plagiarism, you always need to cite the sources you quote, paraphrase, or summarize. Proper citation is crucial for several reasons:
- Giving Credit: Citations give credit to the original authors or creators of ideas, concepts, or information used in your work.
- Avoiding Plagiarism: Plagiarism, the act of using someone else’s work without proper credit, is a serious ethical violation. Citations help you avoid this by clearly indicating what information is from other sources.
- Verifiability: Citations allow readers to trace back the sources you’ve used, helping them to verify the accuracy and validity of your work.
There are different styles set by different universities, academic associations, and publishers, often published in an official handbook with in-depth instructions and examples. Some of the most common citation styles include:
APA
American Psychological Association (APA), widely used in the social sciences, education, and psychology, the APA style emphasizes clear and concise writing, along with proper citation of sources. The 7th edition of the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association provides guidelines for APA style.
APA In-text citation
A brief in-text citation appears within the body of the paper, that identifies the cited work by its author and date of publication. This makes it possible for readers to find the appropriate entry in the reference list at the end of the paper.

APA style uses the author-date citation system, which consists of the author’s last name and the year of publication.
In-text citations can take two forms:
Author type | Parenthetical citation | Narrative citation |
One author | (Smith, 2020) | Smith (2020) |
Two authors | (Jones & Alexander, 2020) | Jones and Alexander (2020) |
Three or more authors | (Martin et al., 2020) | Martin et al. (2020) |
APA Reference List:

APA references generally include information about the author, publication date, title, and source. On the reference page, you only include sources that you have cited in the text (with an in-text citation). You should not include references to personal communications that your reader can’t have access to.
MLA
The Modern Language Association (MLA) referencing style is a widely used format in academic and research writing, primarily within the fields of humanities such as literature, languages, and philosophy. It is the second most used citation style after APA. The latest edition of the MLA Handbook is its 9th edition, published in 2021.
MLA In-text citation
MLA in-text citations are brief references in the body of your research work that lead the reader to the full reference in the Works Cited list. Every time you quote or paraphrase from a source, you must provide an in-text citation.
An MLA in-text citation follows the author’s last name and a page number in parentheses.
Author type | Citation |
One author | (Smith 20) |
Two authors | (Jones and Alexander 20- 25) |
Three or more authors | (Smith et al.20, 34) |
MLA Works Cited List:
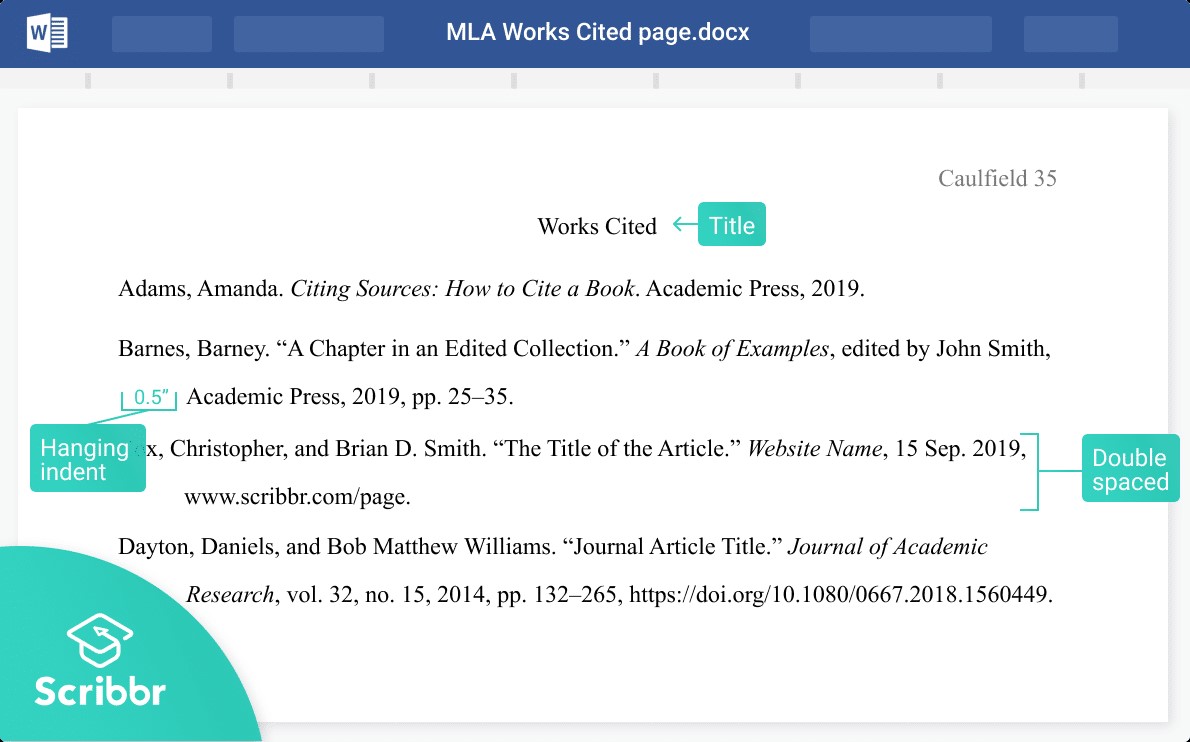
The Works Cited list (also known as reference list or bibliography) gives full details of all sources cited in an MLA in-text citation. It appears at the end of the paper.
APA vs MLA: The Basic Difference

CHICAGO
The Chicago Manual of Style (CMS) is a widely used citation and formatting system commonly used for citing sources in History and occasionally in the Humanities, Sciences, and Social Sciences. It is currently in its 17th edition.
Chicago style has two formats:
- The Notes and Bibliography style is preferred mainly in humanities disciplines, including history, literature, and the arts. Citations are placed in footnotes (bottom of each page) or endnotes (the end of the text) and are usually accompanied by a bibliography listing the sources in full at the end.

Footnotes appear at the bottom of the relevant page. Endnotes appear in a list at the end of the text, just before the reference list or bibliography.


The bibliography lists full references for all the sources cited in the paper. It appears at the end of the paper.
- The Author-Date style (also known as the “Reference List” style) is used in the Sciences. Sources are cited in parenthetical in-text citations and full details are provided in a reference list.
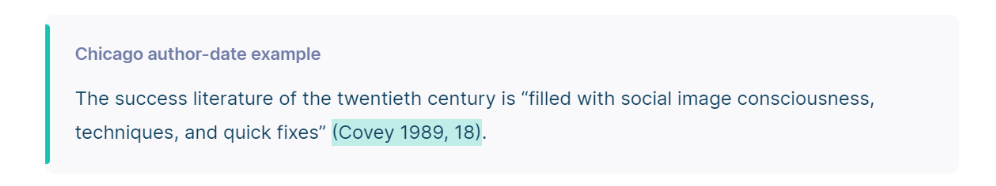
The reference list is like a bibliography only the publication year comes straight after the author’s name.

IEEE
The IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) referencing style is a widely recognized and utilized citation format, particularly in fields related to engineering, computer science, and technology.
IEEE referencing format consists of:
- Numerical in-text citations appearing in brackets.
An IEEE in-text citation consists of a number in square brackets, directing the reader to the relevant reference. If you frequently cite the same source, use the same number each time.

- A numbered reference list with full source information.
The IEEE reference list provides comprehensive details about each source, including authors’ names, title of the source, publication information, and page numbers. The IEEE referencing style is known for its precision and clarity. Its straightforward numbering system simplifies the citation process and is particularly advantageous when dealing with complex technical materials.
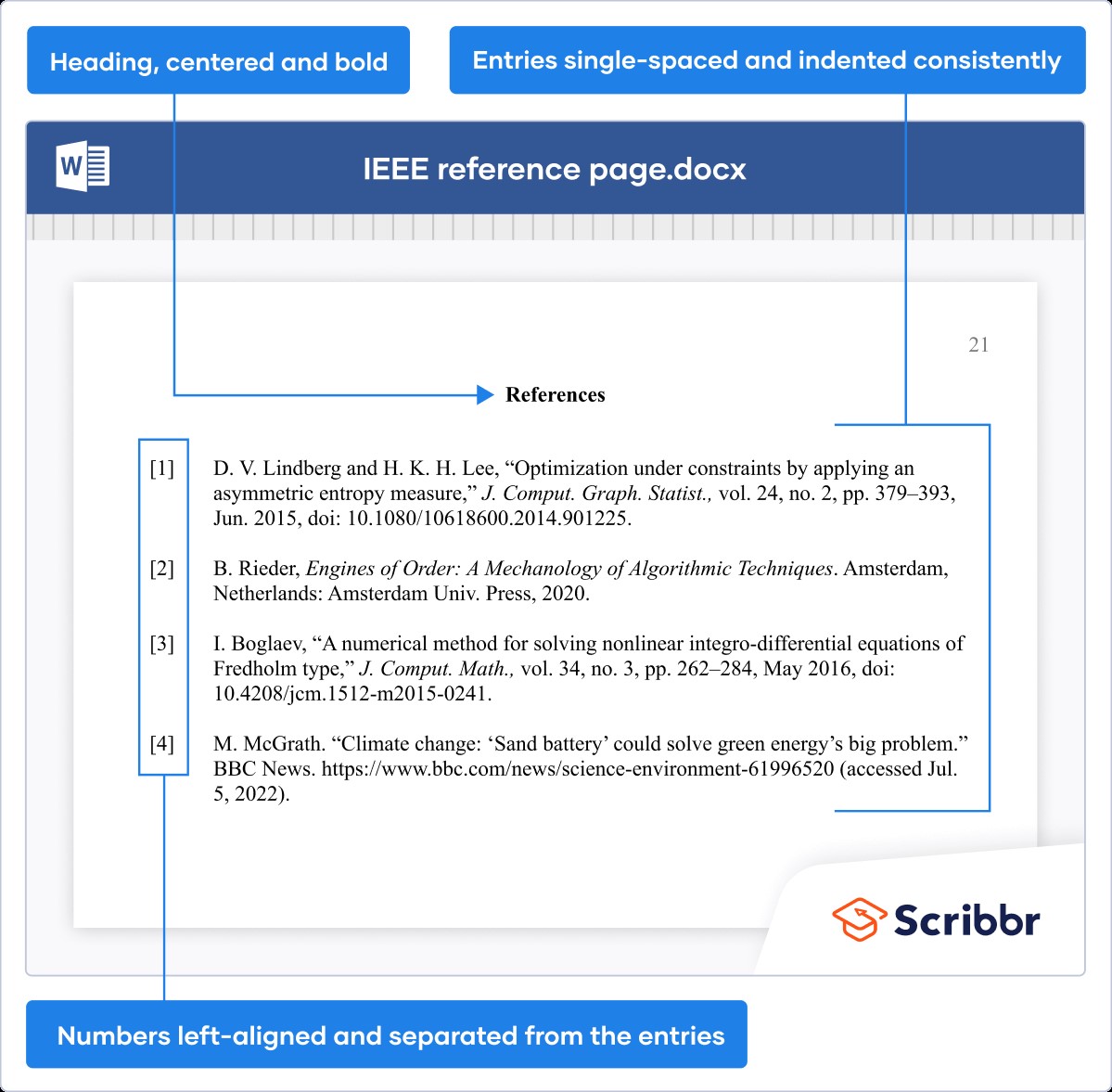
The IEEE reference page appears on a separate page at the end of the paper, with the heading ‘References’ at the top. References are numbered in the order they were first cited in the text.
Blog By : DEEBHA SITHTA
